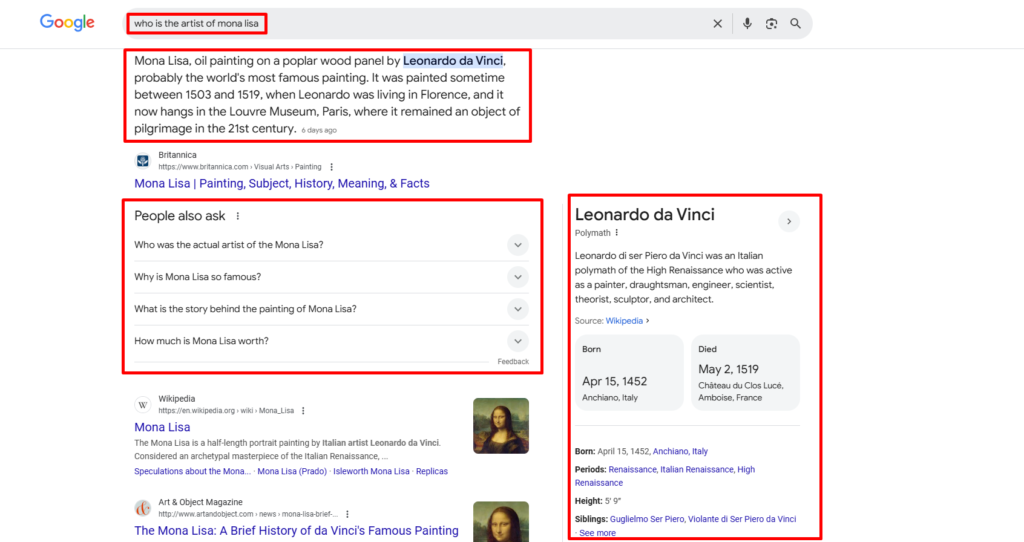
Semantic SEO enhances content ranking by focusing on search intent, context, natural language, and entity relationships rather than isolated keywords. Instead of relying solely on keyword density, Google’s AI-driven algorithms, such as BERT and MUM, analyse queries based on meaning, context, and relevance. This shift enables websites to improve their ranking in semantic SERPs such as featured snippets, knowledge panels, People Also Ask(PAA), and gain visibility in AI Overviews.
By aligning content with semantic search principles, websites can strengthen their position within the semantic web while ensuring that their pages rank for multiple queries rather than just a handful of terms. Those who fail to embrace semantic SEO risk losing visibility to competitors who understand how to structure content effectively for modern search engines.
This guide explores the best methods to optimise your website for semantic SEO, ensuring greater relevance, stronger contextual signals, and improved rankings across Google’s semantic search results. Here are the 13 best ways to optimise your website for semantic search:
- Focus on User Intent and Context
- Implement Structured Data (Schema Markup)
- Optimise for Natural Language & Conversational Queries
- Build a Strong Internal Linking Structure
- Optimise for Entities & Knowledge Graph
- Improve Content Readability & Structure
- Optimise for Voice Search
- Leverage Semantic HTML
- Build Topical Authority
- Optimise for Featured Snippets & Rich Results
- Mobile-First & Page Experience Optimisation
- Leverage AI & NLP for SEO
- Monitor & Improve with SEO Tools
Table of Contents

1. Focus on User Intent and Context
Understanding user intent and context is paramount in Semantic SEO. It goes beyond traditional keyword matching to ensure that the content not only attracts visitors but also satisfies their specific informational needs. By comprehending what users genuinely seek, you can tailor your content to provide the most relevant and engaging answers, thus significantly enhancing user experience and search engine rankings.
To effectively analyse user intent, SEO practitioners rely on detailed search query analysis and direct user feedback. Search query analysis involves examining the phrases and questions that users input into search engines.
This analysis helps to categorise user intent into three primary types: informational, where users are looking for information; navigational, where users are trying to locate a specific website or brand; and transactional, where users intend to perform an action, such as making a purchase. By understanding these patterns, you can optimise your content to meet the exact needs of users at different stages of their journey.
Strategies for aligning website content with identified user intents include creating specific pages that answer direct questions for informational intents, optimising landing pages that guide users smoothly for navigational intents, and enhancing product pages to convert visits into actions for transactional intents. For instance, an informational page might focus on detailed blog posts or articles answering common queries in your field. For navigational intent, ensuring that your brand or service pages are easily accessible and well-linked within your site structure is crucial. Meanwhile, transactional pages should be optimised with clear calls-to-action and streamlined checkout processes to facilitate user transactions.
By focusing on these strategies, websites can create a more tailored browsing experience that directly addresses the varied intentions of their visitors, thereby not only improving site metrics such as bounce rates and conversion rates but also building a stronger, more meaningful connection with their audience. This alignment is essential in the modern SEO landscape, where relevance and user satisfaction are key drivers of search engine rankings.
2. Implement Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Structured data, often referred to as Schema markup, is a critical element of SEO that involves coding your website’s content in a way that search engines can not only crawl but also understand its context more clearly. This coding format helps search engines like Google to interpret the content of your pages and provide more informative results to users through rich snippets, which are enhanced descriptions that appear in search results.
Structured data is a standardised format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content. For example, if you’re posting a recipe, structured data can help convey to search engines what the ingredients are, the cooking time and temperature, the serving size, and more. This clarity allows search engines to display this information in search results in a more engaging and useful way, potentially increasing click-through rates. Here step-by-step guide on implementing schema markup:
- Choose the Right Schema: Determine which type of Schema markup is most relevant to your content or service. Common types include articles, products, events, FAQs and local businesses.
- Generate the Schema Markup: Use a tool like Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper to create the Schema in JSON-LD format. Select your data type, paste in the URL of the page, and start tagging the elements of your page to their respective Schema properties.
- Add the Markup to Your Webpage: Once you’ve generated the Schema markup, embed it in the HTML of your web page. This can typically be done in the head section or in line with the body content, depending on the type of Schema used.
- Test Your Schema: Use tools like Google’s Rich Results Test to check that your Schema markup is correctly implemented and recognised by search engines. This tool will show you what your page will look like in the SERPs and alert you to any errors or improvements that can be made.
Incorporating structured data into your SEO strategy is not just about adhering to best practices; it’s about actively improving the way search engines understand your content, enhancing how your pages are represented in search results, and ultimately driving better, more qualified traffic to your site.
3. Optimise for Natural Language & Conversational Queries
The advent of advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities in search engines signifies a significant shift towards more intuitive and conversational user interactions. This evolution has been largely driven by the increasing use of voice-activated devices and virtual assistants, prompting search engines to prioritise content that aligns with natural speech patterns.
Natural language processing allows search engines to understand and interpret user queries as a human would. This shift has led to a more nuanced approach to search, where the intent behind a query is just as important as the query itself. NLP enables search engines to parse the subtleties of language, including context, tone, and intent, resulting in more accurate and relevant search results. This development means that SEO strategies must now consider not only the keywords but also the conversational context in which those keywords are used. Here are some tips for optimising content to match conversational queries and natural language patterns:
- Use Long-Tail Keywords: Incorporate long-tail keywords that mimic how real people talk and ask questions in everyday conversation. This approach is particularly effective for voice search queries, which tend to be longer and more detailed than text-based searches.
- Write in a Conversational Tone: Craft your content as though you are speaking directly to the reader. Use a friendly, approachable tone that makes your content easily digestible and engaging.
- Answer Questions Directly: Structure your content to answer questions directly and succinctly. Utilise question-based headings and subheadings to make it easier for search engines to extract and feature your content in answer boxes and other rich results.
- Incorporate FAQs: Add a Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section to your website or within articles. This section can directly address common queries related to your topic, formatted with clear, conversational responses.
Some Examples of Content Adjustments That Enhance Alignment with Spoken Queries:
- Before Adjustment: “Tips for better SEO results include using targeted keywords and ensuring mobile compatibility.”
- After Adjustment: “How can I improve my SEO? Start by using targeted keywords that your audience is actually searching for and make sure your website is compatible with mobile devices, as many people browse on these today.”
- Before Adjustment: “The benefits of green tea are many, including weight loss and improved brain function.”
- After Adjustment: “What are the benefits of drinking green tea? Drinking green tea can help you lose weight and improve your brain function, making you feel sharper throughout the day.”
These adjustments not only make the content more relatable and easier for users to understand but also cater to the algorithms that prioritise natural language processing. By optimising your content for natural language and conversational queries, you enhance its visibility and relevance in search results, aligning with the ways users naturally seek information today.
4. Build A Strong Internal Linking Structure
A strong internal linking structure is a cornerstone of effective SEO, offering numerous benefits that can significantly enhance the performance and usability of your website. By strategically linking your site’s content, you not only improve SEO metrics but also provide a better user experience, guiding visitors seamlessly through your website.
Internal links are hyperlinks that point from one page to another within the same domain. These are crucial for SEO for several reasons:
- Enhanced Search Engine Crawling: Internal links help search engines discover new pages on your site. By providing clear paths between pages, you ensure that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your content.
- Improved Page Authority Distribution: Internal linking helps distribute page authority(Pagerank) throughout your site. Pages with high authority can pass on some of that value to other pages when linked, boosting the linked pages’ potential to rank higher.
- Increased Page Views and Lower Bounce Rates: A well-thought-out internal linking strategy can lead to increased page views and reduced bounce rates as users navigate more deeply into your site content.
Here are the Guidelines for Creating an Effective Internal Linking Strategy:
To build a robust internal linking structure, consider the following guidelines:
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: The clickable text in a hyperlink (anchor text) should be informative and relevant to the target page. This not only improves SEO but also aids users in understanding what to expect when they click on a link.
- Create Content Hierarchies: Organise your content in a hierarchical structure with clear categories and subcategories. This organisation will help you establish a logical linking structure that enhances the discoverability of related content.
- Link Deep: Beyond linking to your homepage or contact page, focus on linking to pages that are deep within your site structure. This approach encourages more comprehensive indexing and user exploration of your site.
- Use Relevant Links: Ensure that internal links are contextually relevant to the content they are embedded in. This relevance helps reinforce the semantic relationships between pages, improving SEO performance.
- Regularly Update Internal Links: As you add new content or restructure your site, revisit and update your internal links. This maintenance ensures all links are current and continue to support your site’s SEO strategy.
Internal links significantly enhance topic relevance by clarifying the relationships between different content pieces. For instance, linking to a related article on ‘The Benefits of Green Tea’ from a page discussing ‘Healthy Morning Routines’ can help search engines understand the contextual relationship between these topics, thereby boosting the SEO strength of both pages.
Moreover, a strategic internal linking approach improves user navigation. By providing links to related topics or pages of interest, you help users easily find more content that is relevant to their needs, thereby enhancing their overall site experience. This ease of navigation not only satisfies users but also signals to search engines that your site is well-structured and valuable, further boosting your SEO efforts.
By prioritising a strong internal linking structure, you not only optimise your site for search engines but also create a more cohesive and user-friendly website. This strategic approach is essential for any site looking to improve its SEO performance and user engagement.
5. Optimise for Entities & Knowledge Graph
In the realm of SEO, the importance of entities and their integration into the Knowledge Graph cannot be overstated. Entities are distinct, well-defined concepts or objects that search engines recognise as singular units of knowledge, such as people, places, brands, or products. Understanding and optimising content for these entities is crucial for enhancing visibility and interaction with the Knowledge Graph, a powerful tool used by Google to enhance its search results with enriched, structured information drawn from a variety of sources.
Entities in SEO refer to specific and recognisable subjects or concepts that can be distinctly identified within content. Unlike keywords, which are simply strings of text, entities carry context and attributes that help search engines understand the semantics of web content. The Knowledge Graph takes this information and uses it to create connections between different entities and facts. For instance, the entity “London” might be connected to “River Thames” through the relationship “is located by.” To effectively optimise for entities, follow these steps:
- Entity Identification: Use tools like Google’s Natural Language API to analyse your content and identify potential entities. This tool can help pinpoint which parts of your text are recognised as entities by search engines.
- Research Entity Attributes: Once entities are identified, research their key attributes and relationships to other entities. This can include looking at commonly associated features or the context in which these entities are often discussed.
- Enhance Content with Entity-Specific Information: Integrate these entities naturally into your content. Ensure that the use of entities is relevant and enhances the reader’s understanding. For example, when discussing a historical figure, include key facts that link to other relevant entities, such as their major works, related historical events, or contemporaries.
Now Connecting your content with the Knowledge Graph allows you to leverage a deeper network of semantic relationships, enhancing your content’s visibility and authority. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
- Structured Data Markup: Use schema.org markup to highlight entities within your content. This structured data helps search engines make direct connections between your content and the Knowledge Graph.
- Consistency with Recognised Entities: Ensure that the entities within your content are consistent with those recognised in the Knowledge Graph. This consistency helps reinforce your content’s credibility and relevance.
- Link to Authoritative Sources: When possible, link to authoritative sources that further discuss the entities mentioned in your content. This not only enhances your content’s reliability but also encourages search engines to see your page as a hub of quality information connected to the Knowledge Graph.
By effectively identifying and integrating entities into your content and connecting these with the Knowledge Graph, you can significantly boost your SEO efforts and appear in knowledge panels. This strategy not only improves your site’s visibility but also its perceived relevance and authority, leading to better search rankings and more organic traffic.
6. Improve Content Readability & Structure
Readability is a fundamental aspect of website content that significantly impacts user engagement and SEO performance. When content is easy to read and well-structured, it not only retains visitors longer but also helps search engines understand and rank the content more effectively.
Content readability directly influences how visitors interact with your website. Content that is easy to understand and digest tends to keep visitors on the page longer, reducing bounce rates and increasing the likelihood of conversions. Furthermore, search engines prioritise content that provides a good user experience, which includes clear and accessible information. Thus, improving readability can lead to better SEO rankings as it enhances both user satisfaction and engagement. To enhance the readability of your content, consider the following best practices:
- Use Headers to Organise Content: Headers help break up text into manageable sections that guide readers through your article. Use H1, H2, and H3 tags to structure your content logically, making it easier for both users and search engines to follow the main points of your discussion.
- Employ Bullet Points for Lists: When presenting multiple points, such as benefits, tips, or examples, format them as bullet points. This approach helps readers quickly grasp key information without wading through dense paragraphs.
- Keep Paragraphs Short: Aim for paragraphs that are no more than 3-4 sentences long. Short paragraphs are easier to read and less daunting for readers who may be scanning the content.
- Use Simple Language: Avoid jargon and complex vocabulary unless necessary. Opt for simple language that your audience will easily understand, which enhances the accessibility of your content.
Here are several tools that can help you evaluate and improve the readability of your content:
- Hemingway App: This tool assesses the complexity of your text and suggests simplifications for hard-to-read sentences.
- Grammarly: Beyond grammar checking, Grammarly offers readability scores and stylistic suggestions that can help make your content clearer and more engaging.
- Readability Test Tools: Tools like WebFX’s Readability Tool allow you to input your website URL or text to check for readability scores based on standard tests like the Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level and others.
By regularly using these tools, you can keep your content’s readability in check and ensure that it remains accessible and enjoyable for all users. Remember, the goal is to make your content as user-friendly as possible, which in turn supports your SEO efforts by enhancing engagement and satisfaction.
7. Optimise for Voice Search
Voice search optimisation is becoming increasingly important in the SEO landscape, largely due to the rising popularity of voice-activated devices like smartphones, smart speakers, and virtual assistants. This trend is reshaping how users interact with search engines, making it crucial for SEO strategies to adapt.
Voice search is growing rapidly, driven by improvements in voice recognition technology and the convenience it offers users. People are increasingly relying on voice commands to conduct searches while on the go, which means search queries are becoming more conversational and natural. This shift requires a different approach to content optimisation, as the traditional keyword-focused strategies may not fully capture the intent and nuance of spoken queries. To effectively optimise your content for voice search, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Use Long-Tail Keywords: Voice search queries tend to be longer and more conversational than text-based searches. Incorporate long-tail keywords that mimic how real people talk and ask questions naturally. This practice helps capture the full scope of voice search queries.
- Create Question-Based Content: Since voice searches often come in the form of questions, format your content to answer these directly. Use question phrases such as “What is,” “How to,” “Where can I,” etc., as headings to structure your content and make it more likely to be picked up in voice search results.
- Incorporate Natural Language: Write in a natural, conversational tone that reflects the way people speak. This alignment helps ensure that voice search devices better understand and retrieve your content in response to voice queries.
By focusing on these elements, you can enhance your website’s compatibility with voice search queries, potentially increasing your visibility and accessibility in an era where voice search is becoming the norm. Optimising for voice search involves understanding the unique characteristics of how people use voice commands and integrating this insight into your SEO and content strategy.
8. Leverage Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML plays a crucial role in web development, particularly in enhancing the accessibility and SEO of a website. By using HTML that clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer, websites can achieve better interaction with search engines and users.
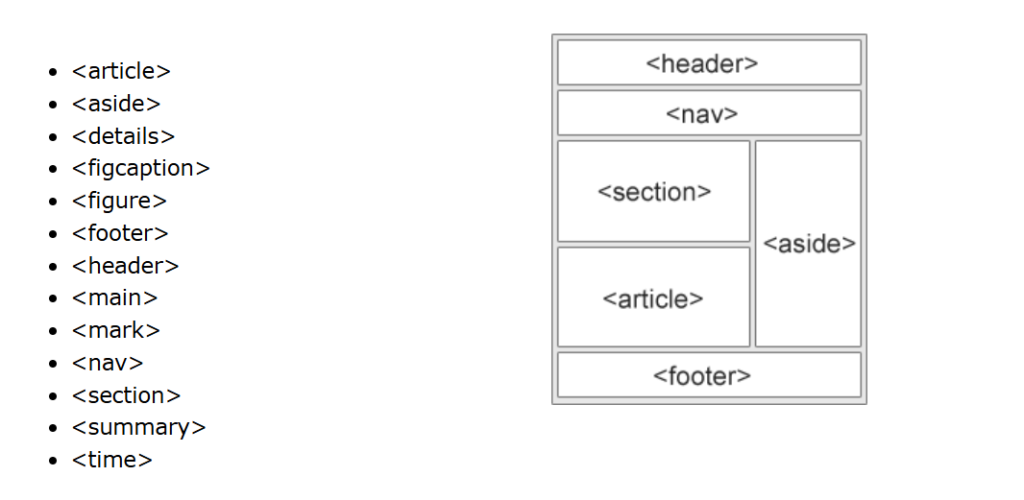
Semantic HTML involves using HTML tags that give information about the content enclosed within the tags, beyond just how they appear on the page. For example, tags like <header>, <footer>, <article>, and <section> describe the purpose of the content, which helps search engines and other assistive technologies understand the structure and significance of information on a webpage. This clarity is beneficial for SEO because it aids search engines in indexing the content more accurately and efficiently, leading to better search engine rankings.
Effective use of semantic HTML tags not only improves content structure but also enhances user navigation and accessibility. Here are some common semantic HTML tags and their uses:
- <article>: This tag is used to enclose a self-contained composition in a document that is independently distributable or reusable. For instance, blog posts, newspaper articles, and user comments can be wrapped in <article> tags.
- <section>: This tag represents a standalone section of a document related to a particular topic. It’s used for grouping themed content, making it easier for search engines to understand different parts of a page.
- <nav>: It indicates navigation links. Using the <nav> tag around major navigation blocks makes it clear to search engines and screen readers that the enclosed links are the primary site navigation elements.
- <header> and <footer>: These tags are used for introductory content or navigational links (header) and for wrapping up information like contact details, copyrights, and related documents (footer).
- <aside>: This tag is used for content that is tangentially related to the content around it, such as sidebars and call-out boxes.
Semantic HTML enhances content discoverability by clearly signalling to search engines what various parts of a web page are about. This clear communication allows search engines to produce more accurate search results and, potentially, rich results that can highlight specific information directly on the search engine results page. For example, proper use of the <article> tag can help search engines understand that a piece of content is a complete and self-contained composition, which might be suitable for direct display in search results.
Furthermore, the use of structured semantic HTML helps create a clear content hierarchy and data relationships, making the website’s content more intelligible and crawlable. This clarity is critical in SEO as it aids in the proper indexing of the website, ensuring that all parts of the site are recognised and appropriately ranked by search engines. By leveraging semantic HTML elements, webmasters can significantly improve their site’s discoverability and user experience, both of which are key factors in achieving optimal search engine rankings.
9. Build Topical Authority
Topical authority has become a cornerstone of effective SEO strategy, fundamentally impacting how websites are perceived by search engines and users alike. By establishing a website as a reliable source of information on specific topics, the website can greatly enhance its search engine visibility and credibility.
Topical authority refers to the recognition a website receives as a credible source of information within a particular field or on a specific subject(niche). Search engines like Google assess topical authority by evaluating the depth, breadth, and quality of content related to specific topics. Websites that demonstrate comprehensive and expert knowledge tend to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), as search algorithms consider them more likely to provide the answer or information that users are seeking. Establishing topical authority involves several focused strategies that collectively enhance a website’s SEO:
- Thorough Content Coverage: Develop a content strategy that comprehensively covers all facets of your topic. This includes creating detailed articles, in-depth guides, and supportive blog posts that collectively address a wide range of user questions and concerns related to the topic.
- External Expert Contributions: Collaborate with industry experts to create or contribute to your content. Having recognised authorities authors or contributors to your articles adds credibility and enhances the trustworthiness of your information. This could involve guest posts, interviews, or co-authored research.
- Consistent Content Updates: Regularly update existing content to reflect the latest information, research, and trends. Keeping your content current is crucial for maintaining topical authority.
By methodically applying these strategies, you can effectively build and maintain topical authority. This not only enhances your SEO but also positions your website as the go-to resource for information on specific subjects, attracting both new and returning users and encouraging greater engagement and interaction.
10. Optimise for Featured Snippets & Rich Results
In the evaluation of SEO, securing a position in featured snippets and rich results can dramatically enhance your website’s visibility and user engagement. These elements in search results provide users with quick, concise answers and information that are directly related to their queries, displayed prominently at the top of search results and the People also Ask section.
Featured snippets are brief excerpts from a web page that directly answer a searcher’s query. They are displayed at the top of Google’s search results and are designed to provide users with quick answers without needing to click through to a website. Rich results, on the other hand, go beyond the standard blue links and include additional data such as images, ratings, and other interactive elements that can help your listings stand out. Both featured snippets and rich results are extracted directly from web pages in Google’s index. To increase your chances of appearing in featured snippets, structure your content with clear, concise, and direct information:
- Use Headers Effectively: Organise your content using descriptive headers (H1, H2, H3) to outline main points and questions. This helps search engines understand the structure of your content and identify sections that directly answer specific queries.
- Incorporate Lists, Tables, and Bullets: For content that involves steps, comparisons, or lists, format it with bullet points or tables. This type of structured data is often pulled into featured snippets because it naturally aligns with the format that featured snippets prefer, which is direct and easy to display in search results.
- Answer Questions Directly: Start sections with clear questions followed by precise answers. For instance, structure a section with a heading like “What is Semantic SEO?” followed by a straightforward, concise paragraph or bulleted list answering the question.
There are certain types of content are more likely to yield rich results, depending on how they are formatted and what information they include:
- Product Pages: Use Schema.org markup to provide details like price, availability, and review ratings. This information can be displayed in rich results, enhancing visibility and click-through rates.
- Recipes: For culinary content, include structured data that details ingredients, cooking time, and nutritional information. Such rich results can feature images, ratings, and even preparation videos.
- Events: Implement structured data for event listings to include essential details like dates, locations, and ticket availability directly in search results.
- FAQ Pages: Format these pages with clear questions and answers and use FAQ schema to help these sections appear directly in rich results, providing immediate value to users searching for quick answers.
By effectively optimising your content for featured snippets and rich results, you can significantly enhance your content’s discoverability and engagement. This not only drives more traffic to your site but also positions your brand as a credible and authoritative source of information in your industry.
11. Mobile-First & Page Experience Optimisation
Mobile-first design and page experience optimisation are critical components of effective SEO. As the majority of users now access the internet via mobile devices, search engines like Google have adjusted their algorithms to prioritise sites that offer a superior mobile experience.
Mobile-first design refers to the practice of designing a website for mobile devices before designing it for a desktop or any other device. This approach is crucial because Google primarily uses the mobile version of the content for indexing and ranking. A mobile-first website ensures that users on mobile devices have seamless and fully functional access to your site, which improves user engagement and retention. Sites that perform well on mobile are more likely to rank higher in search results, as they align with Google’s emphasis on enhancing the mobile user experience.
On the other hand page experience is a set of signals that measure how users perceive the experience of interacting with a web page beyond its pure information value. It includes Core Web Vitals, which are a set of specific factors that Google considers important in a webpage’s overall user experience. Core Web Vitals consist of the following metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. To provide a good user experience, LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of when the page first starts loading.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. To provide a good user experience, pages should have an FID of 100 milliseconds or less.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. To provide a good user experience, pages should maintain a CLS of 0.1. or less.
Checklist for Optimising Mobile-First Design and Page Experience:
- Ensure Responsive Design: Your site should look and function well on a mobile device. Use flexible layouts, images, and CSS media queries to ensure the content displays correctly regardless of screen size or device.
- Optimise Site Speed: Compress files, leverage browser caching, and minimize code to enhance loading times. Fast-loading pages are crucial for keeping mobile users engaged.
- Accessible Design: Make sure that interactive elements are easy to use on a touch screen, and that your site is navigable with one hand.
- Use Mobile-Friendly Test Tools: Regularly test your site with tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to find and fix mobile usability issues.
Tips on Responsive Design and Mobile Usability Testing:
Responsive design is not just about adjusting screen resolutions; it’s about creating entirely flexible and responsive web environments. Here are some tips to enhance mobile responsiveness:
- Flexible Images and Media: Use CSS to control image sizes and ensure they adjust correctly to fit the screen without causing page layout issues.
- Touch-Friendly Elements: Increase the size of buttons and links to make navigation easier on smaller screens.
- Prioritise Above-the-Fold Content: Optimise what users first see when they load your page, keeping crucial content and calls-to-action front and centre.
For mobile usability testing, consider the following:
- Real Device Testing: Test your website on multiple devices to ensure it operates correctly across all potential user scenarios.
- Simulate Different User Conditions: Use tools to simulate different network speeds and conditions to see how your site performs under varying levels of data connectivity.
Optimising for mobile-first design and page experience not only aligns with SEO best practices but also significantly enhances user engagement, which in turn can lead to higher search rankings and better conversion rates.
12. Leverage AI & NLP for SEO
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are revolutionising the field of SEO by enabling more sophisticated and effective content strategies. These technologies help to refine how content is developed, optimised, and personalised, enhancing both the visibility and relevance of web pages in search engine results.
AI and NLP are integral in modern SEO for several reasons. AI enhances data processing and decision-making, allowing for more accurate and dynamic SEO strategies. It analyses large sets of data from search trends and user behaviours to predict which SEO actions will be most effective. Meanwhile, NLP translates human language into something that machines can understand. This capability is crucial for improving semantic search optimisation—ensuring that content is not only keyword-focused but also finely tuned to match the intent and contextual nuances of user queries. Several tools leverage AI and NLP to enhance content optimisation, including:
- Clearscope: Utilizes NLP to help writers create content that is closely aligned with user intent and competitive topics. It provides recommendations for terms, readability, and content structure that are most likely to resonate with target audiences and search engines.
- MarketMuse: Uses AI to analyse content and compare it to similar content on the web, offering suggestions on how to improve topic coverage, keyword integration, and overall content quality to establish topical authority.
- Surfer SEO: Applies AI to analyse SERPs and provides detailed content strategies that align with SEO best practices, including advice on keyword usage, content structure, and other on-page SEO elements.
Integrating AI-driven insights into your content strategy involves several steps:
- Content Gap Analysis: Use AI tools to identify what topics your competitors cover that you do not. These tools can highlight gaps in content that represent opportunities for you to create unique and valuable content.
- Keyword Optimisation: AI can suggest a range of semantically related keywords that may not be obvious but are relevant to your main keywords. This can help you optimise content to answer more user queries and increase your visibility.
- User Intent Mapping: AI tools can analyse search engine result pages and user interactions to determine the intent behind keywords and queries. Integrating these insights helps tailor your content to meet the specific needs and behaviours of your audience.
- Content Personalisation: Use AI to personalise content dynamically based on user data such as past interactions, location, device, and behaviour. This approach can significantly increase engagement and conversion rates.
By leveraging AI and NLP, SEO professionals can not only keep pace with the rapid developments in search engine algorithms but also anticipate future changes. These technologies enable the creation of smarter, more responsive SEO strategies that can adapt to the evolving ways people search for and consume content.
13. Monitor & Improve with SEO Tools
Effective SEO management is a continuous process that requires constant monitoring and adjustment. With the advancement of SEO tools, it’s easier than ever to track performance, understand user behaviour, and refine strategies for optimal outcomes. These tools provide invaluable insights that can drive decisions and foster growth in website traffic and rankings. Several SEO tools are fundamental in the arsenal of any digital marketer, each serving unique functions that aid in different aspects of SEO management:
- Google Analytics: Provides comprehensive data on website traffic, user behaviour, and engagement metrics. It helps you understand where your traffic is coming from, how users interact with your site, and where improvements can be made.
- Google Search Console: Offers tools and reports to help you measure your site’s search traffic and performance, fix issues, and make your site shine in Google Search results. It’s essential for understanding the search terms that bring users to your pages and diagnosing issues related to indexing.
- Ahrefs: A toolset for SEO and marketing running on Big Data. Ahrefs helps you to learn why your competitors rank so high and what you need to do to outrank them. It includes tools for link building, keyword research, competitor analysis, rank tracking, and site audits.
- SEMrush: A comprehensive suite that helps with technical SEO audits, semantic core collection, positioning tracking, and ideas for gaining more organic traffic. It is particularly useful for analysing competitors’ strategies.
- Moz Pro: An all-in-one suite of SEO tools that covers everything from keyword research and link building to site audits and page optimisation recommendations. It’s great for businesses looking to dive deeper into SEO analysis and improvements.
Regular SEO audits are crucial because they provide a detailed review of everything that affects your website’s visibility in search engines. These audits help identify the strengths and weaknesses of your current strategy, allowing for targeted improvements. They can uncover issues such as broken links, poor mobile usability, slow page load times, and semantic markup errors—all of which can impede search engine rankings. Continuous improvement through iterative audits ensures your SEO strategy adapts to algorithm updates and evolving market conditions, maintaining your site’s competitive edge. Interpreting analytics data effectively is key to refining your SEO strategies. Here’s a basic guide to get started:
- Set Clear Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve with your SEO efforts, such as increasing organic traffic, improving bounce rates, or enhancing conversion rates.
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish which metrics will best help you measure the success of your objectives. For SEO, KPIs might include page loading times, SERP rankings, organic traffic levels, and conversion rates from organic search.
- Use Segmentation: Break down your data to examine specific subsets—such as traffic by region or device type. This can help identify trends and issues that are not visible in aggregate data.
- Compare Data Over Time: Look at how your metrics change over time. This will help identify patterns that might be linked to specific SEO actions, seasonal effects, or external factors.
- Act on Insights: Use the insights gained from your analysis to make informed decisions. For example, if you notice that pages with high loading times have higher bounce rates, prioritizing speed optimization could significantly improve user experience and SEO performance.
By regularly utilizing SEO tools to monitor and refine your strategies, you can ensure that your SEO efforts are effective and continue to drive significant value for your business.
What are some of the Best Practices for Semantic SEO?
As search engines continue to evolve, semantic SEO remains a critical component of a successful digital marketing strategy. Semantic SEO refers to the process of building more meaning and context into the content you create, helping search engines understand the nuances of language in your content and how it relates to user queries. In 2025, these practices are more crucial than ever, with search engines using sophisticated AI to better understand and match user intent.
Implement Topic Clustering & Semantic Keyword Optimisation
Topic clustering and semantic keyword optimisation are pivotal in semantic SEO. By organising your content into clusters of related topics, you help search engines understand the context and relationships between different pages, which can significantly enhance your site’s authority and relevance on those topics. For instance:
- Create pillar pages that provide a comprehensive overview of a topic.
- Develop cluster content that addresses specific questions and keywords related to that topic, linking back to the pillar page.
This approach ensures that your website covers a topic thoroughly, from general information down to the nitty-gritty details, which is highly valued by sophisticated search algorithms.
Find Topic or Information Gap from Competitors
Analysing your competitors can reveal valuable insights into content gaps that you can exploit. By identifying and filling these gaps, you can set your content apart and establish your site as a go-to resource for specific information not adequately covered by others. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush can provide competitive analysis that highlights these opportunities.
Find Related Entities and Use Google NLP API Tool
Using tools like Google’s Natural Language Processing (NLP) API can significantly enhance your content’s semantic quality by identifying key entities and their relevance within your content. These entities help tie your content to specific concepts and facts, which search engines use to populate their Knowledge Graphs—enhancing your content’s discoverability and authority.
Create Detailed, High-Quality & User-Friendly Content
Quality content is at the heart of semantic SEO. Your content should not only be detailed and well-researched but also easy to read and understand. High-quality content is more likely to engage readers and encourage them to share, which in turn signals to search engines that your content is valuable and authoritative.
Use N-grams in Content
Incorporating N-grams—sequences of text or words frequently found together—can help improve the contextual relevance of your content. Analysing the use of N-grams can give insights into more natural language patterns that improve content alignment with typical user queries.
Smart Internal Linking for Semantic Relevance
A smart internal linking strategy can bolster your site’s semantic SEO by helping search engines establish informational hierarchies and relationships between different content on your site. Using descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text for internal links can improve user experience and page rankings.
Keep Content Fresh & Continuously Updated
Updating content regularly not only ensures it remains relevant but also shows search engines that your site is active and maintained, which can improve rankings. Refreshing old posts with new information, statistics, or related topics can reinvigorate your content’s appeal and effectiveness.
Create Enticing Metadata & Optimise for Click-Through Rates (CTR)
Metadata still plays a crucial role in semantic SEO by providing clear, concise, and appealing summaries of your web pages in search results. Optimising metadata with high-performing keywords and compelling descriptions can improve your CTR, driving more traffic to your site.
Build Authority with Quality Backlinks & E-E-A-T Principles
Earning high-quality backlinks from reputable sites within your industry can significantly boost your site’s credibility and authority. Additionally, aligning your content with Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) guidelines ensures that your content meets the highest standards of quality and reliability, which is essential for ranking well in search results.
Adopting these best practices for semantic SEO in 2025 will help ensure that your content is well-positioned to meet the sophisticated demands of modern search engines and the users they serve. By focusing on semantic richness, user engagement, and technical SEO, you can improve both your visibility and your competitiveness in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
What is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is the process of building more meaning into the content you create, helping search engines understand the context and nuances of your content, not just the keywords. It involves optimising content to answer more complex queries and focusing on intent matching rather than mere keyword presence. This approach ensures that content can be discovered and accurately interpreted by search engines in a way that matches user intentions and search context.
What is Semantic SERP?
A Semantic Search Engine Results Page (SERP) utilizes the semantic understanding of search queries to generate results that are not just based on keyword matching but on the intent and contextual meaning behind the queries. Search engines like Google use advanced semantic analysis to interpret and fulfil search queries more effectively.
Semantic SERPs typically include:
- Featured Snippets: These are selected search results that are featured on top of Google’s organic results below the ads in a box.
- Knowledge Graphs: These are information boxes that appear on Google when you search for people, places, or things that are widely known and have a notable presence online.
- Related Questions (People Also Ask): A feature that shows other questions asked by users that are related to the search query.
These elements aim to provide users with direct, concise, and highly relevant information without the need for further navigation.
Why is Semantic SEO Important?
Semantic SEO enhances the user experience by providing more relevant and contextually appropriate search results. It improves search accuracy, making sure that users find the content that best answers their questions or fulfils their needs.
Websites that effectively implement semantic SEO are likely to see improved long-term search engine rankings. By aligning content more closely with user intent and providing clear, detailed answers to their questions, sites can achieve better visibility and higher click-through rates.
How Does Google Understand Website Content?
Google uses a combination of algorithms and artificial intelligence technologies, including natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning, to interpret and categorise web content. These technologies help Google grasp not just the literal keywords but also the context and intended meaning behind the content.
Structured data and semantic markup like Schema.org play crucial roles in helping Google understand the themes and contexts of content. By structuring information in a way that search engines can understand, websites can enhance their content’s discoverability and relevance in search results.
How to Optimise Content for Entity-Based SEO?
Entity-based SEO involves identifying key entities (people, places, organisations, etc.) within your content and optimising your content around these entities. This process includes:
- Using structured data to mark up entities on your website.
- Including context around entities to help search engines understand their relevance to the content.
- Leveraging entity relationships to build a more interconnected content strategy that enhances topic authority and depth.
Do SEO Agencies Offer Semantic or Entity SEO Services?
Many SEO agencies now specialise in semantic and entity-based SEO services, recognising their importance in modern SEO strategies. These agencies help businesses improve their online presence by optimising content to align with how search engines now interpret user queries.
Hiring a specialised SEO agency can provide expertise in the latest SEO practices and help businesses stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. They offer strategic insights and tactical execution that leverage semantic SEO principles to improve site rankings and user engagement.
What are the Best SEO Tools for Semantic SEO?
Essential tools for semantic SEO include:
- Ahrefs and SEMrush: For comprehensive keyword research, competitor analysis, and SEO audits.
- Moz Pro: Offers tools for on-page optimization, link analysis, and keyword research.
- Google Search Console and Analytics: For monitoring your site’s performance and understanding user behaviour.
- TextRazor or IBM Watson: Provide advanced NLP capabilities to analyze the structure and semantic quality of content.
These SEO tools help in refining strategies and ensuring content aligns with semantic SEO principles, thereby enhancing content optimization and performance.
Tusar Ahmed is the Founder and Senior SEO Specialist at Inflowen. With over seven years of hands-on experience in SEO, local search optimisation, and keyword strategy, he simplifies complex digital concepts into engaging, actionable insights.
Tusar has worked on 250+ projects across the UK and beyond, helping businesses of all sizes improve their search visibility and achieve measurable growth. His writing blends technical expertise with a clear, approachable tone—making SEO feel both accessible and results-driven.
Follow his content for a fresh, practical perspective on ranking better, reaching the right audience, and staying ahead in the ever-evolving digital landscape.



