Local Competitor analysis is the process of examining the businesses that rank for your target local keywords to understand why they outrank you and how you can do better. This practice is an integral part of any marketing campaign because it keeps your business ahead of the competition. By identifying who your real online competitors are (which may differ from the shop next door) and studying their strategies, you uncover what they’re doing right and where they’re falling short. These insights enable you to replicate their strengths and address gaps in the market.
In this guide, we’ll walk through 10 essential steps for analyzing local SEO competitors – from finding the right rivals and auditing their Google Business Profiles to dissecting their content, citations, reviews, backlinks, and technical setup. Along the way, we’ll highlight why each step matters and how to execute it effectively. By the end, you’ll be equipped with actionable local SEO strategies and local SEO tools to refine your Search Engine Optimization approach and ultimately outrank the competition in local search results.
Table of Contents
1. Identify Your Real Local Competitors
The first step is knowing who you’re really up against online. Your true local SEO competitors aren’t just the familiar businesses across town – they’re the ones dominating search results for your target keywords.
In the digital marketplace, a competitor with greater online visibility can attract your target customers, even if you offer superior products or services. It’s common to discover that the businesses ranking at the top of Google for your service + location queries include companies you hadn’t considered, such as those in adjacent niches or aggressive marketers from outside your immediate area.
You shouldn’t assume you already know all your competitors, because those succeeding in local SERPs could be different from the businesses you see on your street. Identifying the real players in local search sets the foundation for a meaningful analysis – it ensures you focus on outranking the businesses that currently capture the clicks you want.
How to Do It
Start by listing the main keywords related to your business (products or services) and combining them with your target location. Perform Google searches for these terms (e.g. “<service> <location>”) and take note of who appears in the results. Pay special attention to the Google local pack (the map and 3 featured listings at the top of local search results) – the businesses featured there are often your toughest competitors because of their prominent visibility. Also, scroll through the first page of organic results for local directories or other companies that repeatedly show up.
As you compile your list, consider using Google Maps and “near me” searches as well, since proximity can influence results. Be sure to exclude large directory sites like Yelp or TripAdvisor from your competitor list (note them separately as marketing opportunities rather than direct competitors). By the end of this process, you should have a roster of actual local competitors whose online presence is ranking against yours. These are the businesses you’ll be analyzing in the next steps.
2. Build a Competitor Tracking Spreadsheet
With multiple competitors and many data points to compare, keeping everything organized is critical. A dedicated competitor tracking spreadsheet allows you to log each competitor’s information (from rankings and reviews to backlinks and content metrics) in one place. This not only helps you stay organized, but also makes it easier to spot patterns – for example, which competitors appear most frequently across different searches, or which ranking factors correlate with top positions.
Expect to gather a lot of data during your analysis; without a structured spreadsheet, important insights might slip through the cracks. As one guide notes, a comprehensive competitor spreadsheet will include many entries and require sorting through overlaps – it takes time to build, but it’s invaluable for identifying which rivals consistently rank across multiple queries. In short, the spreadsheet is your command center for competitive analysis, ensuring you can systematically track and compare each element of local SEO performance.
How to Do It
Set up a spreadsheet (using Excel or Google Sheets) with columns for the key data you want to track. You might create sections for Google Business Profile (GBP) details, website on-page factors, local citations, reviews, backlinks, and technical SEO metrics for each competitor.
Start by entering the competitors you identified in Step 1. For each competitor, log the keywords you searched and where that competitor ranks (e.g. “Map Pack – #2” or “Organic – #5”) for each keyword. It helps to note the search location or any search personalization factors if relevant.
Next, include columns for metrics like the competitor’s primary GBP category, number of Google reviews (and average rating), any notable GBP features (e.g. “Offers Online Appointments”), and their website URL. As you research further steps, you will fill in additional columns (for example, number of citations found, backlink count, or domain authority, homepage loading speed, etc.).
To manage a growing sheet, consider sorting by competitor name or keyword to see which businesses show up most often – these overlaps indicate a strong competitor worth extra attention. You can start with a small set of your top 3–5 keywords and expand later once you get the hang of it. The goal is to create a living document that you can update over time. This sheet will serve as your reference dashboard for all competitor data, making it much easier to analyze differences and identify opportunities.
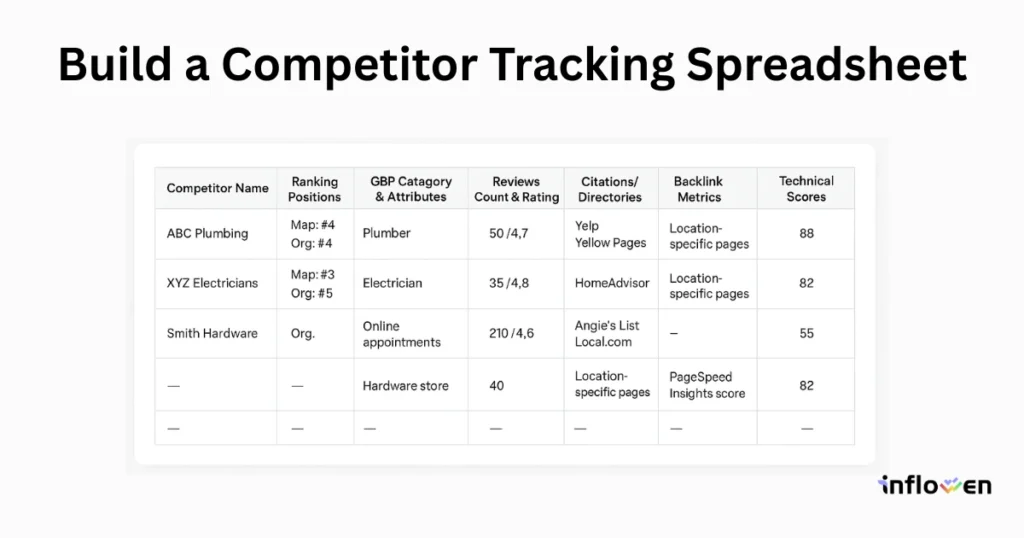
Example: A snippet of a local SEO competitor analysis report, showing top-ranking businesses for a query and key metrics tracked for each (such as citations, backlinks, reviews, and categories). Your competitor spreadsheet can include similar columns to organize such data.
Example Items to Track in the Spreadsheet
To ensure you’re capturing all relevant information, include columns or fields like:
- Competitor Name & Website: The business name and homepage URL (for quick reference).
- Ranking Positions: Their position in the local pack (if applicable) and in organic results for each target keyword.
- GBP Category & Attributes: The primary Google Business Profile category they use, and any special attributes or features displayed (e.g. “Onsite services, Online appointments”).
- Reviews Count & Rating: Number of Google reviews and average star rating on their GBP.
- Citations/Directories: Notable directories or citation sites where the business is listed (Yelp, Yellow Pages, industry-specific directories, etc.).
- Backlink Metrics: Number of backlinks or referring domains (from a tool like Ahrefs), especially local or high-authority links.
- On-Site SEO Notes: Keywords they target on their landing pages, and whether they have location-specific pages.
- Technical Scores: PageSpeed Insights score or mobile-friendliness of their site, if known.
By tracking these items side by side, you can easily compare competitors and see at a glance who excels in which areas.

3. Audit Competitors’ Google Business Profiles (GBP)
Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business) is the cornerstone of local SEO visibility. In fact, GBP signals (like proper categories, NAP info, and engagement) are often cited as the #1 ranking factor for local pack results. For many businesses, the Google Business listing is as important as – or even more important than – their website in attracting local customers. This means that analyzing your competitors’ GBP pages can yield a “treasure trove” of insights.
By examining how top competitors optimize their profiles, you’ll learn what it takes to compete at that level: how many reviews you might need, how often to post updates, which categories or attributes to use, and more. In short, if a rival is outranking you in local search, a significant part of their edge likely comes from a well-optimized GBP. Auditing those profiles shows you exactly why they stand out and gives you a roadmap to improve your own listing.
What to Prioritize When Auditing a GBP?
When reviewing a competitor’s Google Business Profile, focus on the elements that most strongly influence local rankings and user engagement. Key things to examine include:
- Categories & Business Description: Identify the primary category they’ve chosen (and any secondary categories). Are they using relevant, high-value categories for your industry? Also, read their business description for strategic keywords or unique selling points – appropriate categories and keywords here can improve relevance in local search.
- Reviews and Ratings: Note the number of Google reviews they have and their average star rating. A competitor with significantly more positive reviews has an advantage in both rankings and customer trust.
- Photos and Videos: Check the quantity and quality of photos on their profile (and whether they’ve added videos). An active media gallery signals an engaged business. According to Google, “businesses that add photos to their profiles get 42% more requests for directions and 35% more website clicks than those that don’t”.
- Google Posts Frequency: See if they regularly publish Google Posts (updates, offers, or events) and how frequently. Competitors who post weekly or monthly may be keeping their audience engaged and signaling freshness to Google.
- Q&A and Owner Responses: Look at the Q&A section – do they have customer questions posted, and are they answering them? Also, check if the business owner responds to reviews (both positive and negative feedback). High engagement here shows attentiveness.
- Additional Attributes: Note any special attributes listed on their profile (e.g., “Women-led”, “Online appointments”). These can differentiate a business. For example, some service businesses highlight “Onsite services” or “Online appointments” in their listing, which can attract customers looking for those options (see image above).
By prioritizing these GBP elements in your audit, you’ll cover the factors that impact both local ranking prominence and the likelihood of a searcher choosing that business.
How to Do It
Auditing a competitor’s GBP can be done directly on Google. Simply search for the competitor by name (or click their listing from the map pack) to view their full Business Profile. Go through each section of the profile and make notes in your spreadsheet: categories, description text, posts, review count, Q&A entries, etc.
There are also tools to streamline this process. For instance, the GMB Everywhere Chrome extension can extract a business’s categories right from Google Maps, saving you the trouble of guessing their primary and secondary categories. Specialized local SEO tools like BrightLocal or Whitespark offer GBP audit features as well, which can pull data on competitor categories, review stats, and recent posts automatically. Whether manually or with a tool, be thorough in documenting each competitor’s GBP setup.
As you audit, compare their profile to yours. Ask questions like: Have they filled out sections that you haven’t (e.g. added a menu of services, or FAQs)? Are they using a category you overlooked? Do they regularly post Google Updates while your profile is inactive? These comparisons will help pinpoint exactly what you need to do on your own GBP to close the gap.
4. Analyze On-Site Landing Pages
While GBP dominates the map pack, your website’s landing pages play a huge role in local organic rankings and in converting visitors who click through. Any effective competitor analysis will include a close look at competitors’ websites to see how they might be outranking you organically and what content or keywords they’re targeting.
By analyzing on-page factors, you can identify the SEO strategies working for them. For example, you might discover that a competitor has a dedicated page for each service or each neighborhood they serve, filled with localized keywords, which could be one reason their site ranks well for those queries. On-site analysis can also reveal if competitors are doing something unique (like featuring local customer testimonials, embedding Google Maps, or using certain schema markup) that gives them an edge.
Essentially, the content and optimization on competitor landing pages show you what Google favors for those local queries. If your pages are missing these elements, that could be holding you back. Therefore, understanding the differences on-page is key to formulating a plan to outrank them.
How to Do It
Start with the competitors’ pages that rank highest for your target keywords – often this will be their homepage or a specific location/service page. Review the keywords and messaging used on these pages. What keywords do they prominently feature in the title tag, headings (H1, H2s), and body content? These are likely the terms they’ve optimized for, and you’ll want to ensure you’re covering similar (or better) ground on your site. Check if they mention your city or service area in crucial spots (title, headlines, image alt text), as local relevancy on-page can help rankings. Also, observe the depth and quality of the content: Are they providing comprehensive information about the service? Do they answer common customer questions? A competitor page with rich, useful content could satisfy user intent better, thus earning higher SEO marks.
Next, look at their site structure and whether they’ve built out pages that you haven’t. For instance, do they have pages for each neighborhood, suburb, or service variation that you haven’t covered? If you find competitors have location-specific pages or blog posts (like “<Service> in [Neighboring Town]”) that rank, it might indicate an opportunity for you to create similar localized content.
You should also examine elements like internal linking (do they link between related pages to spread link authority?) and calls-to-action or conversion funnels on the page. While conversion optimization isn’t directly a ranking factor, a page that effectively turns visitors into customers (through clear calls-to-action, contact forms, chat widgets, etc.) will ultimately drive more business, and it’s something you might want to emulate if a competitor’s page seems to engage visitors well.
Don’t forget to analyze any structured data on their site. You can use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool on a competitor URL to see if they’re using LocalBusiness schema, review ratings markup, or other schema that could enhance their search listings. If they are, and you’re not, that’s a technical on-page improvement to add to your list (we’ll cover more in Step 9). Finally, assess the user experience: run PageSpeed Insights on their page and yours to compare load times, and check if their site is mobile-friendly and easy to navigate. Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing and fast load times, so a competitor with a smoother, faster site could have an advantage in local SEO. Gather all these observations and feed them back into your strategy – they will inform how you can tweak or overhaul your own landing pages to be more competitive.

5. Assess Local Content Strategy
In SEO, content is king, and this holds true for local search as well. A well-planned and relevant content marketing strategy can set a local business apart from the pack. Consistently creating content that resonates with your local audience serves multiple purposes: it targets long-tail keywords (often boosting organic rankings), showcases your expertise, and builds trust and engagement with customers.
In fact, answering all the questions your customers have about your products or services through content is considered the foundation of modern SEO. By evaluating your competitors’ content efforts, you’ll get insight into how they engage the local community and capture search traffic. You might find, for example, that a competitor runs a popular local blog or produces guides that attract backlinks, contributing to their authority.
Understanding their content strategy helps you identify opportunities for your own content: topics they haven’t covered, formats they’re not using (like videos or infographics), or local angles they’ve missed. Ultimately, strong local content can drive both SEO and brand loyalty, so you want to make sure you’re not leaving this weapon solely in the hands of your rivals.
How to Do It
Take inventory of the types of content your top local competitors are producing. Browse their website for a blog or news section, and see how frequently they update it. Are they publishing articles about local events, neighborhood guides, or community spotlights? Do they post “how-to” articles or tips that relate to your industry and area?
For example, a local home services company might run a blog with seasonal maintenance tips for homeowners in your city. This kind of content not only targets relevant keywords (like “prepare your home for winter in [City]”) but also earns goodwill from local readers. Note any content formats they use: posts, videos, infographics, podcasts, etc. A diversified content strategy can capture different audience preferences.
Next, evaluate content quality and engagement. High-quality, locally-focused content tends to get shared and may earn backlinks from other local sites or social media buzz. If a competitor’s posts have comments or if you find their articles being referenced elsewhere, that’s a sign their content marketing is effective. Identify the topics or themes that seem to resonate. Common ones include local “best of” lists, case studies featuring local clients, or Q&A addressing common customer questions in the area. Make a list of content topics your competitors have covered and then spot the gaps – topics relevant to your business and audience that haven’t been thoroughly covered by competitors. Those gaps are golden opportunities for you to fill with your own content.
Also, pay attention to how competitors leverage local news and events in their content. For instance, if you notice a competitor frequently ties their blog posts into annual local events or seasonal happenings (e.g. a retailer blogging about the upcoming town festival), this may be something you can emulate or do one better. Engaging with local happenings through content can improve your local relevance and show community involvement.
Finally, look beyond just on-site content: check if competitors write guest posts on other local blogs, contribute articles to local newspapers or online magazines, or get mentioned in local press. This often ties into their content strategy and link strategy simultaneously. If they’re investing in content collaborations or PR that you aren’t, consider incorporating that into your plan. By thoroughly assessing what your competitors are talking about – and not talking about – you can craft a local content strategy that not only matches their strengths but also carves out a niche that differentiates your brand.

6. Review Citations and Directory Listings
“Citations” are online mentions of a business’s name, address, and phone number (NAP) – typically in directories and local listing sites. They are a fundamental signal for local SEO. Having consistent NAP citations across reputable sites (like Yelp, Yellow Pages, Apple Maps, industry-specific directories, etc.) helps confirm your business’s legitimacy and geographic relevance to search engines.
In other words, citations strengthen Google’s confidence that your business is truly located where you say it is and is a real local entity. According to one study by Moz, “the accuracy of your citations is a key factor in local search rankings”.
By reviewing where your competitors are listed and the state of their citations, you gain insight into how your own citation profile stacks up. If a competitor is ranking higher, perhaps they are listed on more high-value directories or have cleaner, more consistent NAP information across the web. On the flip side, if you find a top competitor has inconsistencies or missing listings, that’s a weakness you can avoid or exploit. Overall, citation analysis is essential because it impacts local prominence and trust, two things Google evaluates when deciding who to show in the local results.
How to Do It
First, pick a competitor and search for their business name (and address/phone, to be specific) on Google. The goal is to find where their NAP appears online. Manually, you can pair their name with phrases like the city name or “phone” to surface directory listings. You’ll likely find profiles on major platforms (Google Business Profile, Facebook, Yelp, Bing Places, Apple Maps) and industry directories. Take note of each site and record it in your spreadsheet. A quick trick is to search for the competitor’s phone number – since phone numbers are unique, this often brings up directory listings that have that number.
For a more systematic approach, consider using a citation tracker tool (BrightLocal, Whitespark, Moz Local, etc.), which can automatically gather citation information for your business and competitors. These tools will list the directories where a business is cited and even show consistency of NAP formatting. Using a tool can save time and ensure you don’t miss obscure listings.
As you compile the competitor’s citation list, evaluate quality and consistency. Are there any major directories they’re on that you aren’t? If yes, you should plan to get listed there as well. Also, look at the accuracy: Is their name spelled the same everywhere? Do addresses match perfectly (no old addresses or variations), and are phone numbers consistent? If a competitor has super-consistent citations across the board, it might contribute to their local advantage. If you find inconsistencies (say, slightly different addresses or an outdated phone number on some listings), that could be a vulnerability for them – and a reminder for you to keep your citations squeaky clean. Google can get confused by inconsistent NAP info, which may negatively impact rankings, so part of outranking competitors is ensuring you beat them on citation hygiene.
Lastly, identify any niche or local directories your competitors use. For example, a competitor dentist might be listed on a dental-specific directory or a local Chamber of Commerce site. These specialized citations can be very valuable. Mark those down and look into getting your business on them, too. The outcome of this step is a to-do list of directory listings to create or fix for your own business, derived from what you learned about your competitors. By matching or exceeding their citation presence – and maintaining better consistency – you strengthen the foundation of your local SEO.

7. Analyze Review Profiles and Reputation Signals
Customer reviews are hugely influential in local SEO – both for rankings and for converting prospects. Reviews and overall reputation count as a critical factor in establishing trust and local search authority. In fact, industry experts consistently rank review signals (quantity, quality, and velocity of reviews) among the top local ranking factors.
From a customer perspective, a business with a higher average rating and recent positive reviews is more likely to get a click or call. Therefore, analyzing your competitors’ review profiles can highlight what you’re up against in terms of public sentiment and social proof. Do they vastly outrank you in review count? Are they known for stellar customer service (as evidenced by glowing reviews)? Or conversely, do they have negative reviews pointing out consistent problems? All of this is competitive intelligence.
By understanding how customers view your rivals, you can gauge how much work you need to do on your own reputation, and potentially identify weaknesses of theirs that you can capitalize on. Moreover, observing how competitors respond to reviews (or if they respond at all) can inform your reputation management strategy. Engaging with reviews, both good and bad, demonstrates attentiveness and care, which can further set you apart. In short, a strong review profile correlates with better local visibility and customer trust, so you’ll want to know exactly where you stand relative to competitors.
How to Do It
Examine the review profiles of each major competitor on key platforms like Google, Yelp, and Facebook (and any industry-specific review sites relevant to your field). On Google, note the total number of reviews and the average star rating for each competitor – this is usually visible on their GBP listing. Do the same for Yelp (taking into account Yelp’s different rating scale and filtering). Record these in your spreadsheet.
Next, assess the review sentiment and content. Skim through a sample of recent reviews to identify what customers praise or complain about. Are there recurring positive themes (e.g. “quick response time”, “friendly staff”) that you should also emphasize in your service? Are there common complaints (e.g. “long wait times” or “parking is difficult”) that perhaps your business handles better, which you could highlight in your marketing?
Pay equal attention to positive and negative reviews – both offer valuable insights. Positive reviews tell you what matters most to customers (make sure you continue to excel in those areas), while negative reviews often reveal competitor weaknesses or gaps in service that you might exploit. For instance, if several reviews mention that a competitor doesn’t offer a certain product or has limited scheduling availability, and you can shine in that area, that’s a competitive differentiator to the market. Also, see how competitors handle their negative feedback: Do they ignore criticism, or do they respond promptly with attempts to resolve issues? A competitor who consistently has unresolved negative reviews might be alienating customers, some of whom could be won over by your business if you demonstrate better care.
Also, analyze review recency and velocity. A competitor with a steady stream of recent reviews is actively engaging customers (or asking for feedback) and staying fresh in Google’s eyes, whereas one with outdated reviews might not. Identify if any competitor is particularly aggressive in reputation management. For example, some businesses may encourage happy customers to leave Google reviews (resulting in a high count), or they might be responding to every single review. Take notes on these practices.
Finally, don’t limit your analysis to Google. Check if competitors have testimonials on their website, or reviews on their Facebook pages, Better Business Bureau profiles, or other relevant platforms (for example, TripAdvisor for hospitality, ZocDoc for healthcare, etc.). A truly dominant local competitor will tend to have a strong reputation across multiple platforms. By cataloging the reputation landscape, you’ll get a clear picture of where you need to focus – be it getting more reviews, improving your rating, responding more actively, or all of the above. Remember, customer feedback is essentially a public report card for each business, so use this step to learn what you can do to earn straight A’s.
8. Perform Backlink Profile Comparison
Backlinks – links from other websites to your site – remain an important factor for SEO, including local SEO. They serve as “votes of confidence” in the eyes of search engines. By examining competitors’ backlink profiles, you can discover how they might be leveraging off-site SEO to outrank you.
In local SEO, quality matters more than quantity: a few backlinks from authoritative, local-relevant sources (like a popular local newspaper or a chamber of commerce directory) can significantly boost credibility. If a competitor has managed to get featured on local blogs, news sites, or community pages, those backlinks could be bolstering their rankings and local prominence. Likewise, analyzing backlinks can reveal partnerships or sponsorships competitors are engaged in (for example, a link from a local charity event page might indicate they were a sponsor). This step is crucial because it helps you identify link-building opportunities for your own site.
You might find websites linking to your competitors that could potentially link to you as well if you approach them (this is often called the “link intersect” technique). Furthermore, if a competitor’s link profile is weak and yours is stronger, that’s a signal you can capitalize on your advantage by continuing to build links and possibly overtaking them.
How to Do It
Use an SEO tool with backlink analysis capabilities (such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz, or others) to pull the backlink profile for each major competitor’s domain. Focus on the metrics and details that matter: the number of referring domains, the quality of those domains (look at domain authority or similar metrics), and the relevance of linking sites. List out some of the most authoritative or notable sites linking to each competitor. Are they getting links from local news articles, bloggers, industry associations, or perhaps sponsorships (like a Little League team page acknowledging sponsors)? For example, a competitor might have a backlink from localcitynews.com due to a featured story – that’s something you’d want to note and consider pursuing for your business.
Identify any local-specific backlinks. These are links from websites that are specific to your city/region (like event calendars, local directories, or community organizations). They’re particularly valuable because they signal local relevance. If competitor A has five local .gov or .edu links and you have none, that could be a difference-maker. Also look at anchor text if possible – do the links use local keywords (like “dentist in [City]”) or just the business name? This can sometimes hint at the SEO intent behind the links.
While reviewing, ask “How did they likely get this link?” and categorize it: Is it a link they earned through content (like a blog post of theirs got cited)? Through relationships (they are a member of a business network)? Through listings (a directory inclusion)? Or even possibly through self-created means (guest posting, etc.)? Not all backlinks are replicable, but many are. For instance, if three competitors are all listed on a certain local business directory or niche resource that you weren’t aware of, you should plan to get your business listed there too. If a competitor has a guest post on “IndustryInsider.com”, maybe you could write one as well or pitch a similar industry site.
Also consider setting up alerts or using a “link intersect” feature (some tools have this) to find sites that link to multiple of your competitors but not to you. Those are prime link prospects because they clearly are willing to link to businesses like yours. Competitive backlink monitoring is not only about one-time analysis; it can also be ongoing. As one source notes, keeping an eye on competitor backlinks can uncover new link-building opportunities and even potential business partnerships over time. Use the insights from this analysis to formulate an outreach and link acquisition plan. By matching competitors’ strong backlinks and finding a few unique ones of your own, you can build a more robust link profile that helps propel you above them in rankings.
9. Compare Technical and On-Site SEO Factors
Technical and on-site SEO elements – such as site speed, mobile usability, site architecture, and schema markup – can significantly impact your search rankings and user experience. If two competitors have similarly strong content and backlinks, the one with better technical optimization often wins out (and provides a smoother experience to visitors, leading to more engagement and conversions).
Google has made it clear that factors like mobile-friendliness and page load speed matter; for instance, Google now uses a mobile-first index and considers Core Web Vitals (loading speed, interactivity, stability) as ranking signals. So, if a competitor’s website is faster and more mobile-friendly than yours, they could have a hidden edge contributing to their higher ranking.
Additionally, technical elements like proper use of structured data (schema) might give their listing more visibility (think star ratings showing on SERPs, or business hours appearing) and improve click-through rates. Technical SEO issues on your site (broken links, poor navigation, missing meta tags, etc.) can also hurt your performance. Therefore, part of outranking competitors is ensuring your site meets or exceeds the technical quality of theirs. By comparing these factors, you pinpoint any technical weaknesses to fix and potentially spot tactics competitors are using that you can adopt.
How to Do It
Perform a basic technical audit of both your site and your competitors’ sites. Some steps you can take include:
- PageSpeed Comparison: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to test your homepage and a key landing page, then do the same for a competitor’s pages. Look at the scores and the recommendations. Is their site significantly faster? Does it perform better on mobile, especially? If a competitor consistently scores, say, in the 90s for performance while your site is lagging in the 60s, that’s a sign you need to speed up. Faster load times not only please users but also reduce bounce rates, indirectly benefiting SEO.
- Mobile-Friendly Test: Open the competitors’ sites on your phone. Check if the site layout is responsive and easy to navigate on a small screen. Are buttons easily clickable? Is the text readable without zooming? A site might rank lower if it’s not mobile-optimized. If your site struggles on mobile where it shines, it’s imperative to improve your mobile UX.
- Structured Data and Rich Snippets: As mentioned earlier, run competitors’ pages through Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Validator to detect any structured data. Common local schemas include LocalBusiness (with details like address, hours, coordinates), Review/AggregateRating for showing star ratings, and FAQ schema for Q&A sections. If a competitor is using schema markup effectively and you’re not, they could be enjoying enhanced listings (like rich snippets) that draw more clicks. For example, a competitor might have star ratings showing under their Google result because they marked up their customer reviews – that extra visual can attract clicks. Take note of any schema types they use. Implementing a similar schema on your site can help search engines understand your content better and possibly reward you with richer search result displays.
- Site Architecture & On-Page Elements: Evaluate how the competitor’s site is structured. Do they have a clear menu and hierarchy of pages? How many clicks to get from the homepage to important content? A well-structured site helps distribute link equity and is easier for Google to crawl. Compare on-page SEO basics too: Are their title tags and meta descriptions well-crafted with local keywords? Do they have descriptive, keyword-rich URLs? While these elements might seem basic, they collectively contribute to SEO. If you find competitors consistently have more optimized titles or headers, make sure to refine yours accordingly.
- Other Technical Signals: Look for HTTPS usage (all sites should be secure; if a competitor isn’t, that’s an area you naturally win, but if you aren’t secure and they are, migrate to HTTPS ASAP). Check for any obvious errors like broken links or missing images on their site versus yours. Tools like Screaming Frog can crawl a site and identify issues; you could crawl your competitors’ sites (with appropriate settings to not overburden them) to see if they have a cleaner technical bill of health than you do.
Make a list of all technical or on-site differences you discover. For instance, maybe you find your site is slower and also missing FAQ schema that two competitors have implemented. These go into your action plan. Many technical fixes are “low-hanging fruit” in the sense that once you spot them, you can improve them on your site and potentially see quick benefits.

10. Monitor Competitor Rankings Over Time
Analyzing competitors isn’t a one-and-done task – the local search landscape can change rapidly. New competitors can emerge, and existing ones can update their strategies (e.g. a rival might suddenly gain 50 new reviews or invest in a website revamp that boosts their rankings). To consistently outrank competitors, you need to continuously monitor the situation. By tracking competitor rankings over time, you’ll notice trends: who is moving up, who is dropping, and how algorithm updates or seasonal changes affect the pack. This step is essentially about staying proactive – if you see a competitor making gains, you can respond before they completely overtake you.
Likewise, if you deploy a new strategy (say, you improved your GBP and built new backlinks), monitoring will show whether it’s helping you rise relative to others. Regular monitoring also helps in identifying any new players in your SEO space. Perhaps a business that wasn’t on your radar before starts ranking in the top 3; you’d want to know that ASAP to include them in your analysis.
How to Do It
Use a rank tracking tool or software to keep tabs on your most important local keywords and the competitors’ positions. Many SEO tools (like SEMrush, Ahrefs, BrightLocal, Moz, etc.) have rank tracking features where you can input keywords and specify a location to track local rankings. Even Google’s own tools like Google Search Console can give you an idea of your performance, but they won’t directly show competitors – that’s where third-party tools shine. For local tracking, consider tools that support tracking the local pack as well as organic results. Some tools (for example, BrightLocal’s Local Search Grid) offer a visual grid of rankings across a map, which can be very insightful for seeing how competitors rank at varying distances from the search location. At minimum, set up a weekly or monthly report that logs the top rankings for your target search terms.
In your competitor tracking spreadsheet, dedicate a section to periodic ranking updates. For instance, each month, note who holds the #1, #2, #3 spots for “<keyword> + <city>” in both the map pack and organic. Over time, you’ll build a history that might reveal, for example, a competitor climbing steadily from #5 to #2. If you spot such a trend, you can dig into what they’ve done recently (did they suddenly get a bunch of new reviews or a new website?) and react accordingly. Also, watch your own movements – if you slip from #1 to #3 one week, which competitor(s) outranked you, and what changed? Perhaps their site became faster or they added a new landing page; the clues often tie back to the factors we’ve discussed in steps 1–9.
Apart from rankings, consider monitoring other key metrics that signal competitive shifts. Keep an eye on competitors’ review counts over time (set a reminder to check their Google review number every month or use a tool that alerts you to new reviews on their profile). Sudden spikes might coincide with improved rankings. Monitor their content activity – e.g. did a competitor start blogging monthly, whereas before they didn’t? Tools like RSS readers or content change detectors can alert you to new content on competitor sites. You might also set up Google Alerts for competitor brand names to catch news or press releases about them (which could bring new backlinks).
The main idea is to stay informed. Local SEO is indeed an ongoing process requiring vigilance. By tracking competitors, you’ll be able to adapt your strategy in real-time, whether that means ramping up your own review acquisition, adjusting your keywords, or launching new promotions to counter theirs. Regular monitoring ensures that you maintain the gains from your hard work and continue to stay one step ahead of your competition.
Why Should You Conduct a Local SEO Competitor Analysis?
Conducting a local SEO competitor analysis isn’t just an optional extra – it’s a necessity if you want to excel in local search. In any community or service area, multiple businesses are vying for the same customers and visibility. Without understanding your rivals’ strategies, you’re essentially flying blind.
By contrast, a thorough competitor analysis lets you pinpoint exactly who is outranking you and why, so you can make informed improvements. In fact, for SEO professionals, digging into competitor strengths and weaknesses is considered a cornerstone of a winning local campaign. It reveals the gap between your current performance and your competitors’ – whether it’s fewer reviews, slower site speed, missing content topics, or other factors – and thus highlights where you should focus your efforts.
Moreover, competitor analysis helps you stay ahead of industry trends and customer expectations. By examining competitors, you often learn more about your target market: what services or features customers value (by reading competitor reviews and content), pricing or offerings others have introduced, and new keywords or platforms that are emerging. This knowledge is power. As one guide noted, the goal of local competitor analysis is to identify why those competitors are ranking high in Google Maps/Local Pack and how you can capture those same opportunities.
What are some of the best tools or software to check local search competitors?
Analyzing local search competitors can be time-consuming, but thankfully, there are many tools designed to simplify the job. For example, all-in-one local SEO platforms like BrightLocal and Whitespark offer toolkits specifically for competitor research – they can identify who your local competitors are, audit their Google Business Profiles, track their citation listings, and even monitor their rankings on a map grid. SEO suites such as SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz also have features to help with competitor analysis: you can compare domain authority, backlink profiles, and find keyword gaps between your site and competitors.
For tracking rankings in different locations or on mobile versus desktop, tools like GeoRanker or Local Falcon allow you to see how competitors rank at various points in your city. Additionally, Google’s own tools shouldn’t be overlooked – Google Business Profile Insights (within your GBP dashboard) can sometimes show how you stack up in terms of search views, and using Google Maps with location set to your area can give a quick manual look at the top-rated competitors. To delve into competitor reviews and reputation, platforms like ReviewTrackers or Google Alerts (for alerting to new reviews or mentions) can be useful. In summary, there’s a range of software for different aspects of competitor analysis. Many are highlighted in this list of 11 local SEO tools – exploring those will help you find the right mix of tools to gain insights on your local rivals efficiently.
How to Create a Local SEO Strategy to Outrank Your Competitors?
Outranking local competitors requires not just analysis, but a well-crafted strategy that puts your findings into action. Start by addressing all major factors we’ve discussed: optimize your Google Business Profile (choose the best categories, regularly post updates, gather reviews), ensure your website is fully optimized (with localized content, fast mobile-friendly pages, and strong on-page SEO), and work on building local links and citations to boost your site’s authority.
A key part of your strategy should be to leverage the weaknesses you discovered in competitors – for instance, if they lack a certain type of content or have poor engagement with customers, make that an area where you shine. Equally, try to match or exceed their strengths; if a top competitor posts a new blog article weekly, consider doing the same or more with even higher-quality content.
Remember that local SEO is not a set-and-forget effort, but an ongoing cycle of implementation, measurement, and adjustment. Track your progress (rankings, traffic, leads) as you roll out changes, and be ready to adapt if something isn’t working or if a competitor makes a new move. Ultimately, a winning local SEO strategy is one that addresses all the ranking signals – from technical SEO and content to reviews and engagement – in a cohesive plan tailored to your business. For a detailed walkthrough on building such a strategy, check out this guide on 15 local SEO strategies, which provides step-by-step tactics to help you systematically surpass your local competitors.
Tusar Ahmed is the Founder and Senior SEO Specialist at Inflowen. With over seven years of hands-on experience in SEO, local search optimisation, and keyword strategy, he simplifies complex digital concepts into engaging, actionable insights.
Tusar has worked on 250+ projects across the UK and beyond, helping businesses of all sizes improve their search visibility and achieve measurable growth. His writing blends technical expertise with a clear, approachable tone—making SEO feel both accessible and results-driven.
Follow his content for a fresh, practical perspective on ranking better, reaching the right audience, and staying ahead in the ever-evolving digital landscape.



